
Heart DNA Test
The Heart DNA Test is a cutting-edge genetic testing product designed to assess your risk of developing heart disease. This test uses a simple saliva sample to analyze your DNA and determine your genetic predisposition to various heart health conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and coronary artery disease. The results of the test can help you and your doctor make informed decisions about your heart health and take steps to reduce your risk of developing heart disease.
The Heart DNA Test is non-invasive and can be completed in the comfort of your own home. Simply provide a saliva sample, send it back to the laboratory, and receive your personalized report within a few weeks. The report will provide you with an in-depth analysis of your genetic predisposition to heart disease, as well as recommendations for lifestyle changes and monitoring that can help you maintain optimal heart health.
With the Heart DNA Test, you have the opportunity to take control of your heart health and reduce your risk of developing heart disease. This test is a valuable tool for anyone who wants to understand their genetic predisposition to heart health conditions and make proactive changes to improve their overall well-being.
This test measures your Cardiac genetic risk towards:
✔️ Atrial Fibrillation
✔️ Coronary Artery Disease
✔️ Myocardial Infarction
✔️ Hypertension
✔️ Peripheral Arterial Disease
✔️ Sickle Cell Anaemia
✔️ Type III Hyperlipoproteinemia
Your genetic propensity towards metabolising:
✔️ Triglycerides
✔️ HDL and LDL Cholesterol
Your innate body response to the following medications:
✔️ Perindopril Metabolism (ACE inhibitor)
✔️ Beta-blockers Sensitivity
✔️ Beta-Blockers Metabolism
✔️ Verapamil Metabolism (Calcium Channel Blocker)
✔️ Verapamil vs Atenolol
✔️ Beta-blockers and Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Response
✔️ Warfarin Sensitivity
✔️ Clopidogrel Metabolism
✔️ Statin Induced Myopathy
Your genetic risk for developing blood clots:
✔️ Venous Thrombosis
✔️ Homocysteine and Oestrogen Supplements Risk
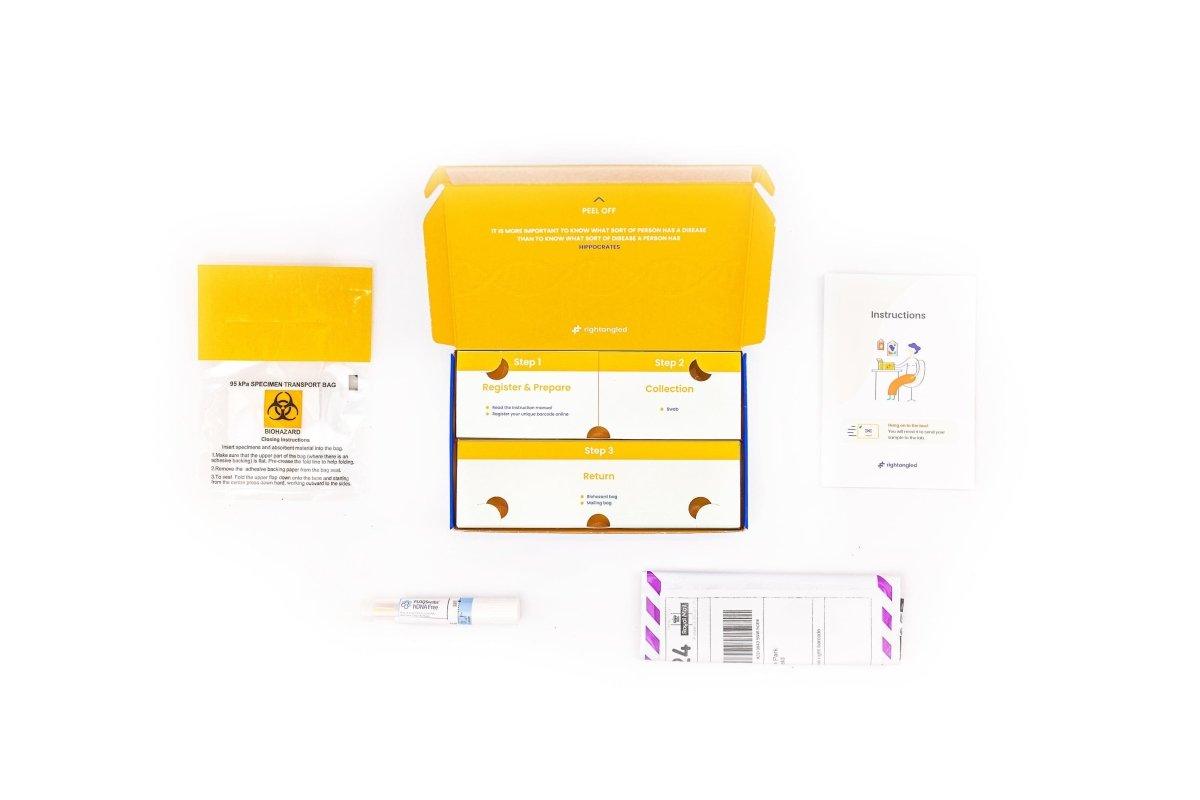
Sample collection method:
💦 Cheek swab
Couldn't load pickup availability
Pickup available at Rightangled HQ
Usually ready in 24 hoursPairs well with
If you have any questions, you are always welcome to contact us. We'll get back to you as soon as possible, within 24 hours on weekdays.
Contact Us
Reach out to us with any questions or feedback. Our team is available via email at info@rightangled.com to ensure you get the support you need.
Shipping Information
Receive your orders quickly and reliably. Choose from multiple delivery options at checkout for convenience and speed. All orders placed before 3 pm are processed on the same day.
Customer Support
Our dedicated team is here to help you every step of the way. Contact us for assistance with orders, tests, or any other inquiries. We are available Monday to Friday between 8 am and 5 pm, and on Saturdays between 9 am and 1 pm.
FAQ’s
Find answers to commonly asked questions about our services, tests, and procedures. Our help centre proovides quick solutions and detailed information.
How it works
Share information about your brand with your customers. Describe a product, make announcements, or welcome customers to your store.


Test details
Cardiovascular Risk Analysis
Fats (Lipid) Metabolism
Heart Medications Response
Blood Clot Risk Analysis
Tested biomarkers
FAQs
Please read our FAQs page to find out more.
